
2022
Orawit Thinnukool
In computer vision, object recognition and image categorization have proven to be difficult challenges. They have, nevertheless, generated responses to a wide range of difficult issues from a variety of fields. Convolution Neural Networks (CNNs) have recently been identified as the most widely proposed deep learning (DL) algorithms in the literature. CNNs have unquestionably delivered cutting-edge achievements, particularly in the areas of image classification, speech recognition, and video processing. However, it has been noticed that the CNN-training assignment demands a large amount of data, which is in low supply, especially in the medical industry, and as a result, the training process takes longer. In this paper, we describe an attention-aware CNN architecture for classifying chest X-ray images to diagnose Pneumonia in order to address the aforementioned difficulties. Attention Modules provide attention-aware properties to the Attention Network. The attention-aware features of various modules alter as the layers become deeper. Using a bottom-up top-down feedforward structure, the feedforward and feedback attention processes are integrated into a single feedforward process inside each attention module.
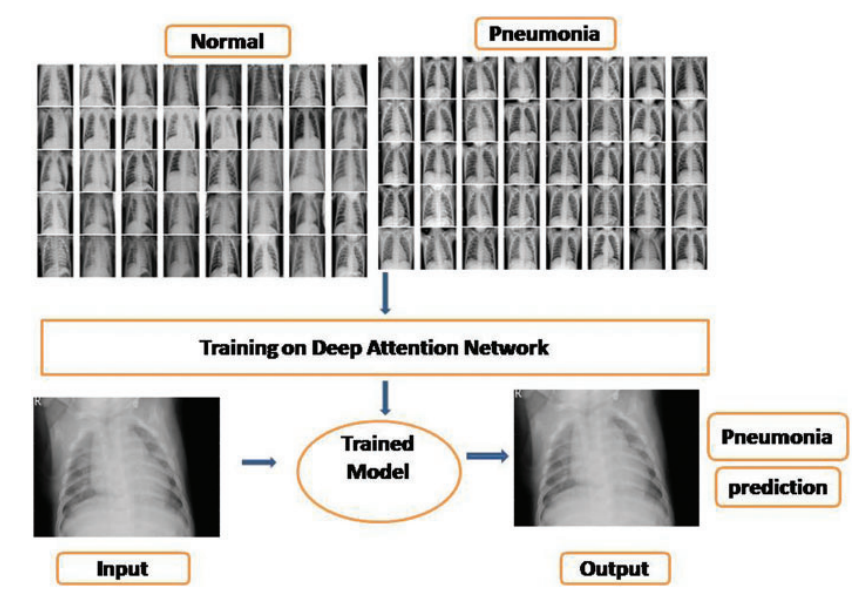
In the present work, a deep neural network (DNN) is combined with an attention mechanism to test the prediction of Pneumonia disease using chest X-ray pictures. To produce attention-aware features, the suggested network was built by merging channel and spatial attention modules in DNN architecture. With this network, we worked on a publicly available Kaggle chest X-ray dataset. Extensive testing was carried out to validate the suggested model. In the experimental results, we attained an accuracy of 95.47% and an F- score of 0.92, indicating that the suggested model outperformed against the baseline models.
2022
Phasit Charoenkwan
Progesterone receptors (PRs) are implicated in various cancers since their presence/absence can determine clinical outcomes. The overstimulation of progesterone can facilitate oncogenesis and thus, its modulation through PR inhibition is urgently needed. To address this issue, a novel stacked ensemble learning approach (termed StackPR) is presented for fast, accurate, and large-scale identification of PR antagonists using only SMILES notation without the need for 3D structural information. We employed six popular machine learning (ML) algorithms (i.e., logistic regression, partial least squares, k-nearest neighbor, support vector machine, extremely randomized trees, and random forest) coupled with twelve conventional molecular descriptors to create 72 baseline models. Then, a genetic algorithm in conjunction with the self-assessment-report approach was utilized to determine m out of the 72 baseline models as means of developing the final meta-predictor using the stacking strategy and tenfold cross-validation test. Experimental results on the independent test dataset show that StackPR achieved impressive predictive performance with an accuracy of 0.966 and Matthew’s coefficient correlation of 0.925. In addition, analysis based on the SHapley Additive exPlanation algorithm and molecular docking indicates that aliphatic hydrocarbons and nitrogen-containing substructures were the most important features for having PR antagonist activity. Finally, we implemented an online webserver using StackPR, which is freely accessible at http://pmlabstack.pythonanywhere.com/StackPR. StackPR is anticipated to be a powerful computational tool for the large-scale identification of unknown PR antagonist candidates for follow-up experimental validation.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-20143-5
2022
Phasit Charoenkwan
Amyloid proteins have the ability to form insoluble fibril aggregates that have important pathogenic effects in many tissues. Such amyloidoses are prominently associated with common diseases such as type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease. There are many types of amyloid proteins, and some proteins that form amyloid aggregates when in a misfolded state. It is difficult to identify such amyloid proteins and their pathogenic properties, but a new and effective approach is by developing effective bioinformatics tools. While several machine learning (ML)-based models for in silico identification of amyloid proteins have been proposed, their predictive performance is limited. In this study, we present AMYPred-FRL, a novel meta-predictor that uses a feature representation learning approach to achieve more accurate amyloid protein identification. AMYPred-FRL combined six well-known ML algorithms (extremely randomized tree, extreme gradient boosting, k-nearest neighbor, logistic regression, random forest, and support vector machine) with ten different sequence-based feature descriptors to generate 60 probabilistic features (PFs), as opposed to state-of-the-art methods developed by a single feature-based approach. A logistic regression recursive feature elimination (LR-RFE) method was used to find the optimal m number of 60 PFs in order to improve the predictive performance. Finally, using the meta-predictor approach, the 20 selected PFs were fed into a logistic regression method to create the final hybrid model (AMYPred-FRL). Both cross-validation and independent tests showed that AMYPred-FRL achieved superior predictive performance than its constituent baseline models. In an extensive independent test, AMYPred-FRL outperformed the existing methods by 5.5% and 16.1%, respectively, with accuracy and MCC of 0.873 and 0.710. To expedite high-throughput prediction, a user-friendly web server of AMYPred-FRL is freely available at http://pmlabstack.pythonanywhere.com/AMYPred-FRL. It is anticipated that AMYPred-FRL will be a useful tool in helping researchers to identify new amyloid proteins.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-11897-z
2022
Phasit Charoenkwan
Fast and accurate identification of phage virion proteins (PVPs) would greatly aid facilitation of antibacterial drug discovery and development. Although, several research efforts based on machine learning (ML) methods have been made for in silico identification of PVPs, these methods have certain limitations. Therefore, in this study, we propose a new computational approach, termed SCORPION, (StaCking-based Predictior fOR Phage VIrion PrOteiNs), to accurately identify PVPs using only protein primary sequences. Specifically, we explored comprehensive 13 different feature descriptors from different aspects (i.e., compositional information, composition-transition-distribution information, position-specific information and physicochemical properties) with 10 popular ML algorithms to construct a pool of optimal baseline models. These optimal baseline models were then used to generate probabilistic features (PFs) and considered as a new feature vector. Finally, we utilized a two-step feature selection strategy to determine the optimal PF feature vector and used this feature vector to develop a stacked model (SCORPION). Both tenfold cross-validation and independent test results indicate that SCORPION achieves superior predictive performance than its constitute baseline models and existing methods. We anticipate SCORPION will serve as a useful tool for the cost-effective and large-scale screening of new PVPs. The source codes and datasets for this work are available for downloading in the GitHub repository (https://github.com/saeed344/SCORPION).
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-08173-5
2022
Phasit Charoenkwan
Antimalarial peptides (AMAPs) varying in length, amino acid composition, charge, conformational structure, hydrophobicity, and amphipathicity reflect their diversity in antimalarial mechanisms. Due to the worldwide major health problem concerning antimicrobial resistance, these peptides possess great therapeutic value owing to their low incidences of drug resistance as compared to conventional antibiotics. Although well-known experimental methods are able to precisely determine the antimalarial activity of peptides, these methods are still time-consuming and costly. Thus, machine learning (ML)-based methods that are capable of identifying AMAPs rapidly by using only sequence information would be beneficial for the high-throughput identification of AMAPs. In this study, we propose the first computational model (termed iAMAP-SCM) for the large-scale identification and characterization of peptides with antimalarial activity by using only sequence information. Specifically, we employed an interpretable scoring card method (SCM) to develop iAMAP-SCM and estimate propensities of 20 amino acids and 400 dipeptides to be AMAPs in a supervised manner. Experimental results showed that iAMAP-SCM could achieve a maximum accuracy and Matthew's coefficient correlation of 0.957 and 0.834, respectively, on the independent test dataset. In addition, SCM-derived propensities of 20 amino acids and selected physicochemical properties were used to provide an understanding of the functional mechanisms of AMAPs. Finally, a user-friendly online computational platform of iAMAP-SCM is publicly available at http://pmlabstack.pythonanywhere.com/iAMAP-SCM. The iAMAP-SCM predictor is anticipated to assist experimental scientists in the high-throughput identification of potential AMAP candidates for the treatment of malaria and other clinical applications.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsomega.2c04465
2022
Phasit Charoenkwan
Objectives: To develop a machine learning (ML)-based framework using red blood cell (RBC) parameters for the prediction of the α+-thalassemia trait (α+-thal trait) and to compare the diagnostic performance with a conventional method using a single RBC parameter or a combination of RBC parameters. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on possible couples at risk for fetus with hemoglobin H (Hb H disease). Subjects with molecularly confirmed normal status (not thalassemia), α+-thal trait, and two-allele α-thalassemia mutation were included. Clinical parameters (age and gender) and RBC parameters (Hb, Hct, MCV, MCH, MCHC, RDW, and RBC count) obtained from their antenatal thalassemia screen were retrieved and analyzed using a machine learning (ML)-based framework and a conventional method. The performance of α+-thal trait prediction was evaluated. Results: In total, 594 cases (female/male: 330/264, mean age: 29.7 ± 6.6 years) were included in the analysis. There were 229 normal controls, 160 cases with the α+-thalassemia trait, and 205 cases in the two-allele α-thalassemia mutation category, respectively. The ML-derived model improved the diagnostic performance, giving a sensitivity of 80% and specificity of 81%. The experimental results indicated that DeepThal achieved a better performance compared with other ML-based methods in terms of the independent test dataset, with an accuracy of 80.77%, sensitivity of 70.59%, and the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) of 0.608. Of all the red blood cell parameters, MCH < 28.95 pg as a single parameter had the highest performance in predicting the α+-thal trait with the AUC of 0.857 and 95% CI of 0.816–0.899. The combination model derived from the binary logistic regression analysis exhibited improved performance with the AUC of 0.868 and 95% CI of 0.830–0.906, giving a sensitivity of 80.1% and specificity of 75.1%. Conclusions: The performance of DeepThal in terms of the independent test dataset is sufficient to demonstrate that DeepThal is capable of accurately predicting the α+-thal trait. It is anticipated that DeepThal will be a useful tool for the scientific community in the large-scale prediction of the α+-thal trait.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36362531/
2022
Phasit Charoenkwan
Discovery of potential drugs requires rapid and precise identification of drug targets. Although traditional experimental methodologies can accurately identify drug targets, they are time-consuming and inappropriate for high-throughput screening. Computational approaches based on machine learning (ML) algorithms can expedite the prediction of druggable proteins; however, the performance of the existing computational methods remains unsatisfactory.
This study proposes a computational tool, SPIDER, to enhance the accurate prediction of druggable proteins. SPIDER employs various feature descriptors pertaining to several aspects, including physicochemical properties, compositional information, and composition-transition-distribution information, coupled with well-known ML algorithms to facilitate the construction of the final meta-predictor. The experimental results showed that SPIDER enabled more precise and robust prediction of druggable proteins than the baseline models and current existing methods in terms of the independent test dataset.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/sdfe/reader/pii/S2589004222011555/pdf
2022
Phasit Charoenkwan
Staphylococcus aureus is deemed to be one of the major causes of hospital and community-acquired infections, especially in methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains. Because antimicrobial peptides have captured attention as novel drug candidates due to their rapid and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, anti-MRSA peptides have emerged as potential therapeutics for the treatment of bacterial infections. Although experimental approaches can precisely identify anti-MRSA peptides, they are usually cost-ineffective and labor-intensive. Therefore, computational approaches that are able to identify and characterize anti-MRSA peptides by using sequence information are highly desirable. In this study, we present the first computational approach (termed SCMRSA) for identifying and characterizing anti-MRSA peptides by using sequence information without the use of 3D structural information. In SCMRSA, we employed an interpretable scoring card method (SCM) coupled with the estimated propensity scores of 400 dipeptides. Comparative experiments indicated that SCMRSA was more effective and could outperform several machine learning-based classifiers with an accuracy of 0.960 and Matthews correlation coefficient of 0.848 on the independent test data set. In addition, we employed the SCMRSA-derived propensity scores to provide a more in-depth explanation regarding the functional mechanisms of anti-MRSA peptides. Finally, in order to serve community-wide use of the proposed SCMRSA, we established a user-friendly webserver which can be accessed online at http://pmlabstack.pythonanywhere.com/SCMRSA. SCMRSA is anticipated to be an open-source and useful tool for screening and identifying novel anti-MRSA peptides for follow-up experimental studies.
2022
Phasit Charoenkwan
Tumor homing peptides (THPs) play a crucial role in recognizing and specifically binding to cancer cells. Although experimental approaches can facilitate the precise identification of THPs, they are usually time-consuming, labor-intensive, and not cost-effective. However, computational approaches can identify THPs by utilizing sequence information alone, thus highlighting their great potential for large-scale identification of THPs. Herein, we propose NEPTUNE, a novel computational approach for the accurate and large-scale identification of THPs from sequence information. Specifically, we constructed variant baseline models from multiple feature encoding schemes coupled with six popular machine learning algorithms. Subsequently, we comprehensively assessed and investigated the effects of these baseline models on THP prediction. Finally, the probabilistic information generated by the optimal baseline models is fed into a support vector machine-based classifier to construct the final meta-predictor (NEPTUNE). Cross-validation and independent tests demonstrated that NEPTUNE achieved superior performance for THP prediction compared with its constituent baseline models and the existing methods. Moreover, we employed the powerful SHapley additive exPlanations method to improve the interpretation of NEPTUNE and elucidate the most important features for identifying THPs. Finally, we implemented an online web server using NEPTUNE, which is available at http://pmlabstack.pythonanywhere.com/NEPTUNE. NEPTUNE could be beneficial for the large-scale identification of unknown THP candidates for follow-up experimental validation.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0010482522004826
2022
Phasit Charoenkwan
The development of efficient and effective bioinformatics tools and pipelines for identifying peptides with dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory activities from large-scale protein datasets is of great importance for the discovery and development of potential and promising antidiabetic drugs. In this study, we present a novel stacking-based ensemble learning predictor (termed StackDPPIV) designed for identification of DPP-IV inhibitory peptides. Unlike the existing method, which is based on single-feature-based methods, we combined five popular machine learning algorithms in conjunction with ten different feature encodings from multiple perspectives to generate a pool of various baseline models. Subsequently, the probabilistic features derived from these baseline models were systematically integrated and deemed as new feature representations. Finally, in order to improve the predictive performance, the genetic algorithm based on the self-assessment-report was utilized to determine a set of informative probabilistic features and then used the optimal one for developing the final meta-predictor (StackDPPIV). Experiment results demonstrated that StackDPPIV could outperform its constituent baseline models on both the training and independent datasets. Furthermore, StackDPPIV achieved an accuracy of 0.891, MCC of 0.784 and AUC of 0.961, which were 9.4%, 19.0% and 11.4%, respectively, higher than that of the existing method on the independent test. Feature analysis demonstrated that our feature representations had more discriminative ability as compared to conventional feature descriptors, which highlights the combination of different features was essential for the performance improvement. In order to implement the proposed predictor, we had built a user-friendly online web server at http://pmlabstack.pythonanywhere.com/StackDPPIV.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1046202321002711
2021
Orawit Thinnukool
The brain tumor is a deadly disease that is caused by the abnormal growth of brain cells, which affects the human blood cells and nerves. Timely and precise detection of brain tumors is an important task to avoid complex and painful treatment procedures, as it can assist doctors in surgical planning. Manual brain tumor detection is a time-consuming activity and highly dependent on the availability of area experts.
Therefore, it is a need of the hour to design accurate automated systems for the detection and classification of various types of brain tumors. However, the exact localization and categorization of brain tumors is a challenging job due to extensive variations in their size, position, and structure. To deal with the challenges, we have presented a novel approach, namely, DenseNet-41-based CornerNet framework.
The proposed solution comprises three steps. Initially, we develop annotations to locate the exact region of interest. In the second step, a custom CornerNet with DenseNet-41 as a base network is introduced to extract the deep features from the suspected samples. In the last step, the one-stage detector CornerNet is employed to locate and classify several brain tumors. To evaluate the proposed method, we have utilized two databases, namely, the Figshare and Brain MRI datasets, and attained an average accuracy of 98.8% and 98.5%, respectively. Both qualitative and quantitative analysis show that our approach is more proficient and consistent with detecting and classifying various types of brain tumors than other latest technique .
2021
Orawit Thinnukool
we propose a novel computerised approach in this work using deep learning and featuring an ant colony optimisation (ACO) based selection. The proposed method consists of four fundamental steps: data augmentation to solve the imbalanced dataset, fine-tuned pre-trained deep learning models (NasNet Mobile and MobileNet-V2), the fusion of extracted deep features using matrix length, and finally, a selection of the best features using a hybrid ACO and a Neighbourhood Component Analysis (NCA). The best-selected features were eventually passed to many classifiers for final recognition. The experimental process involved an augmented dataset and achieved an average accuracy of 99.7%. Comparison with existing techniques showed that the proposed method was effective.
2021
Orawit Thinnukool
In this study, futuristic and emerging innovations are analyzed, improving COVID-19 effects for the general public. Large data sets need to be advanced so that extensive models related to deep analysis can be used to combat Coronavirus infection, which can be done by applying Artificial intelligence techniques such as Natural Language Processing (NLP), Machine Learning (ML), and Computer vision to varying processing files. This article aims to furnish variation sets of innovations that can be utilized to eliminate COVID-19 and serve as a resource for the coming generations. At last, elaboration associated with future state-of-the-art technologies and the attainable sectors of AI methodologies has been mentioned concerning the post-COVID-19 world to enable the different ideas for dealing with the pandemic-based difficulties.
2021
Pradorn Sureephong
Water, an essential resource for crop production, is becoming increasingly scarce, while cropland continues to expand due to the world’s population growth. Proper irrigation scheduling has been shown to help farmers improve crop yield and quality, resulting in more sustainable water consumption. Soil Moisture (SM), which indicates the amount of water in the soil, is one of the most important crop irrigation parameters. In terms of water usage optimization and crop yield, estimating future soil moisture (forecasting) is an essentially valuable task for crop irrigation. As a result, farmers can base crop irrigation decisions on this parameter. Sensors can be used to estimate this value in real time, which may assist farmers in deciding whether or not to irrigate. The soil moisture value provided by the sensors, on the other hand, is instantaneous and cannot be used to directly compute irrigation parameters such as the best timing or the required water quantity to irrigate. The soil moisture value can, in fact, vary greatly depending on factors such as humidity, weather, and time. Using machine learning methods, these parameters can be used to predict soil moisture levels in the near future. This paper proposes a new Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM)-based model to forecast soil moisture values in the future based on parameters collected from various sensors as a potential solution. To train and validate this model, a real-world dataset containing a set of parameters related to weather forecasting, soil moisture, and other related parameters was collected using smart sensors installed in a greenhouse in Chiang Mai province, Thailand. Preliminary results show that our LSTM-based model performs well in predicting soil moisture with a 0.72% RMSE error and a 0.52% cross-validation error (LSTM), and our Bi-LSTM model with a 0.76% RMSE error and a 0.57% cross-validation error. In the future, we aim to test and validate this model on other similar datasets.

Lecturer
Patison Palee

Assistant Professor
Sirikorn Santirojanakul

Assistant Professor
Noppon Choosri

Assistant Professor
Pattama Longani

Assistant Professor
Chartchai Doung sa-ard

Lecturer
Krittawaya Thongkoo

Lecturer
Kannika Daungcharone

Lecturer
Pachara Tinamas

Lecturer
Keattikorn Samarnggoon

Lecturer
Thepparit Sinthamrongruk

Lecturer
Supara Grudpan

Assistant Professor
Orawit Thinnukool

Lecturer
Noppon Wongta
2022
Chalermpon Kongjit
A UCD was utilised to construct a process taxonomy to understand, analyse, design and develop an application suitable for Thai women. It was found from an evaluation of the currently-available womens m-health applications that usability is their main weakness; therefore, this aspect needed to be prioritised in the new design.

2021
Acrapol Nimmolrat

2021
Acrapol Nimmolrat
2020
Orawit Thinnukool
The triage application will be utilised to support the pre-hospital process and to classify patients conditions before they are admitted to the Emergency Department (ED). The application is suitable for users who are not medical emergency staff. Patients with non-trauma symptoms may be a suitable group to use the application in terms of time used to identify IDC for their own symptoms. The use of the application can be beneficial for those who wish to self-identify their symptoms before requesting medical services.
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=th.ac.cmu.camt.triage&hl=th&gl=US
2022
Teerawat Kamnardsiri
Background: Clavicular and scapular orientations vary between neck pain patients as do clinical features and responses (changes in pain and rotation range) to scapular repositioning. Associations between these factors are unknown. Objectives: To identify subgroups of neck pain patients based on three-dimensional (3D) measures of clavicular and scapular orientations and differences between subgroups in clinical characteristics and responses to scapular repositioning. Design: Cross-sectional study. Methods: Eligible participants were recruited as part of a larger study. 
2021
Pradorn Sureephong
Crop lifecycle management is important for crop care and maintenance throughout its life. The existing recommendation and expert systems do not provide advice for the entire crop lifecycle. However, each stage of the crop's lifecycle necessitates a different set of recommendations. As a result, this paper proposed a recommendation system based on sensor data and rule-based extraction from expert people to provide crop management advice throughout its lifecycle. The proposed system's rules are built around IF-THEN situations. The proposed system will analyze the data by searching for relationships between input data and rule-based using a PHP script to define the best recommendation for farmers. This proposed system was put into action in a greenhouse dome in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Farmers were overwhelmingly pleased with it, giving it a 96% satisfaction rating.
https://journalmodernpm.com/jmpm/article/view/JMPM02717

Assistant Professor
Teeraporn Saeheaw

Assistant Professor
Pitipong Yodmongkol

Assistant Professor
Jirawit Yanchinda

Lecturer
Danaitun Pongpatcharatrontep

Assistant Professor
Sirikorn Santirojanakul

Lecturer
Acrapol Nimmolrat

Lecturer
Chalermpon Kongjit

Assistant Professor
Manissaward Jintapitak

Associate Professor
Ratapol Wudhikarn

Lecturer
Suepphong Chernbumroong
2022
Chalermpon Kongjit
The situation of the covid-19 epidemic is a driving force of the global market's demand increase of electronic devices and parts. Entire electronic component manufacturers, especially the transformer manufacturing industry, which is a device that supplies power to many electronic devices, encounters problems in producing products that are unable to keep up with the quickly increasing demand. This research aims to increase the productivity of small transformers by lean approach. The paper depicts processes relevant to improving production processes, reducing waste, and finding unnecessary processes. The method begins with two actions. First, study the current situation in transformer manufacturing of a case study. Second, study the customer order to delivery process using the Value Stream Mapping (VSM) and analyze entire processes of transformer manufacturing to identify standard time by unit work. The main technique is for measuring working time by timing the forward motion with the time measurement method version 2 (MTM-2). The Cause and Effect diagram was displayed with improving guidelines on two operations. First the concept of lean manufacturing was used in principal role, second the ECRS technique (Eliminate, Combine, Rearrange and Simplify) was applied to reduce "waste"as well as to optimize and reduce the manufacturing process of the transformer. The results lead to an increase in the final product per hour from 45 pieces per hour to 75 pieces per hour which increases up to 30% per hour. In addition, the productivity improvements increased the productivity of 3.46 workers per hour to 6.82 per hour (increase of 97.11%) and production time was reduced from 1,109 seconds to 229 seconds (73.04% of productivity).
https://journals.utm.my/aej/article/view/16712
2022
Chalermpon Kongjit
In Thailand, the achievement of English learners has been disappointing, despite the constant efforts to develop English education, and there is an urgent need for Thai learners to focus on the pronunciation of English. The research identified Thai English learners’ specific English pronunciation problems. It also designed and facilitated a new self-directed learning process for learners to improve their English pronunciation, which is based on a combination of a community of practice (CoP) and self-directed learning. There were 15 participants selected purposively involved in this study. This study demonstrated how to use new learning process to identify specific problems and shares how to solve problems by practicing among participants so that the objectives can be reached. The new learning process was useful in helping users to improve their English pronunciation to communicate effectively in real life. The new learning process also can be used for other language learners.
https://ijere.iaescore.com/index.php/IJERE/article/view/22195
2021
Teerawat Kamnardsiri
Background: The constructive and specific feedback in guiding long jump athletes to improve their performance in each phase is part of the critical process for achieving desired long jump distance. However, to date, the potential approach for assisting a coach in capturing long jump movement and transferring their knowledge to long jump students is not well-established. Objectives: To investigate the performance of long jump students and evaluate transferring knowledge from coaches to long jump students using a Knowledge-Based Smart Trainer (KBST) System. 
Methods: Twenty-two participants (fifteen males, mean age = 15.33 ± 1.95 years; seven females, mean age = 14.57 ± 2.07 years) participated in the study. All participants were recruited from eleven sports schools in Thailand. Each participant was instructed to perform the long jump movement, including running, take-off, and landing, for three attempts (Test 1, Test 2, and Test 3). Test 1 was the conventional approach (coaches provided the feedback based on their experience). Test 2 and Test 3 were the KBST system approach (coaches provided the feedback based on the results from KBST system). Two cameras were used to record the participant movement from the starting position to the landing position. The capture data were analyzed by KBST system program. The outcome measures were starting position, maximum velocity, maximum velocity position, and take-off angle. Repeated-Measures ANOVA was conducted to compare the long jump performance across the three trials. The statistical significance was set at p-value < 0.05. Results: There was a statistically significant difference between Test 1 and Test 3 for long jump distance (mean difference = 0.292; Std. Error = 0.129; Sig. = 0.34). However, the mean of take-off angle was similar across the three trials (Test 1 = 12.16°, Test 2 = 12.71°, and Test 3 = 12.95°, respectively). Conclusion: The KBST system was effective in improving long jump students’ performance and also transferring knowledge from the coach to long jump students.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2021.609114/full

Lecturer
Konlawat Klaynak

Lecturer
Arus Kunkhet,

Assistant Professor
Manissaward Jintapitak

Lecturer
Sumet Yordkaew

Lecturer
Setthee Boonchoo

Lecturer
Nat Chantasingh

Lecturer
Thunyapruet Fongdawirat

Lecturer
Suparada Prapawong

Lecturer
Nop Kongdee

Lecturer
Khongthat Thongphun

Lecturer
Keattikorn Samarnggoon

Assistant Professor
Teerawat Kamnardsiri

Lecturer
Supara Grudpan

Lecturer
Noppon Wongta
2022
Disaya Chudasri
Traditional craftsmanship is one of the seven domains that represent the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Thailand (ICH) (Intangible Cultural Heritage.
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-16-9472-1_14
2021
Teerawat Kamnardsiri
Background: Declines in physical and cognitive functions are recognized as important risk factors for falls in older adults. Promising evidence suggests that interactive game-based systems that allow simultaneous physical and cognitive exercise are a potential approach to enhance exercise adherence and reduce fall risk in older adults. However, a limited number of studies have reported the development of a combined physical-cognitive game-based training system for fall risk reduction in older adults. Objective: The aim of this study is to develop and evaluate the usability of an interactive physical-cognitive game-based training system (game-based exercise) for older adults.

https://games.jmir.org/2021/4/e27848/
2020
Patison Palee


https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1386505619308603

Lecturer
Danaitun Pongpatcharatrontep

Lecturer
Pakinee Ariya

Lecturer
Acrapol Nimmolrat

Lecturer
Achara Khamaksorn

Assistant Professor
Raslapat Suteeca

Lecturer
Arinya Pongwat

Lecturer
Boontarika Paphawasit

Assistant Professor
Vorathamon Cherapanukorn

Lecturer
Khanita Tumphasuwan

Lecturer
Wantana Areeprayolkij

Assistant Professor
Pradorn Sureephong
2022
Achara Khamaksorn
International joint ventures (IJVs) are a specific type of strategic alliance between contractors from developed and developing countries and have been increasingly used. IJVs between multinational organisations are considered a successful strategy to benefit from international market opportunities in the globalised world. International construction joint ventures (ICJVs) have become of significant interest as the global construction market continues to be integrated into the more competitive business environment. The aim of this article is to uncover the knowledge transfer (KT) practices in an ICJV using social network analysis (SNA). The case presented here is the pilot study. A total of 19 questionnaire surveys were undertaken with selected team members. UCINET 6.0, an SNA package, was used to analyse the collected data and NetDraw was used to visualise the sociogram. This article first presents the actors' attributes; then, social network characteristics, which consist of network structure, network density and degree of centrality and cliques of actors, are presented. This analysis will be used to identify the key actors that influence the KT processes in this case study.
2022
Vorathamon Cherapanukorn
In order to survive and gain competitive advantages in the post COVID-19 pandemic, tourism destinations should plan their business strategy by focusing on customer expectation. A number of research have studied tourist satisfaction, particularly, hotels and transports, however there is limited investigation with tourist attractions which have different prominence from other tourism service providers. The purpose of this study was to identify the tourists’ satisfaction components for tourist attractions by adopting an opinion mining technique and using the zero-shot text classification method. The total of 40,000 online tourists’ reviews from 40 tourist attractions in Thailand, that were posted up thought TripAdivisor.com between 2010 and 2021, were analyzed. The research findings reveal six components of tourist attraction satisfaction (TATSAT) model that includes 1) ambiance, 2) hospitality, 3) price, 4) accessibility, 5) cleanliness, and 6) security. All attributes of TATSAT model are generated from tourists’ point of view and was analyzed by the focus group discussion with five tourism experts from both academics and practitioners. This model expands the idea of HOLSAT and SERVQUAL by focusing on the tourist attraction business sector. The results can serve academics and practitioners in the research and improvement of tourist satisfaction to maximize competitive advantages for tourist attraction sector in the future.
https://journals.aserspublishing.eu/jemt/article/view/6893
2022
Arinya Pongwat
Purpose: This paper aims to assess the various impacts of tourism development in Chiang Mai on the local populace’s sense of well-being. The moderating effect of employment in and affiliation with the tourism industry on perception of tourism development is also examined. Design/methodology/approach: A sequential explanatory mixed method design is adopted, beginning with the development of a conceptual model that links residents’ perceived impact of tourism development with their general and life domain-specific well-beings. The model is tested with a survey of 567 respondents who are long-term residents of Chiang Mai. The findings are subsequently used in the semi-structured in-depth interviews with selected tourism stakeholders to provide qualitative explanation and meaning to the data. Findings: The results suggest a reciprocal relationship between perceived economic, cultural and environmental impact of tourism development and Chiang Mai residents’ general sense of well-being. It also revealed that community well-being and material well-being accounted the most and the least, respectively, on overall well-being for Chiang Mai residents. Another interesting observation was that Chiang Mai residents feel the same way about the various perceived impact of tourism development on overall sense of well-being, regardless of whether they are employed or affiliated with the tourism industry or otherwise. Originality/value: With limited literature on the perceived impact of tourism development by residents in Asia, this research provides a Thai perspective of the said impact on general well-being. A sequential explanatory mixed method provides an added lens to induce insights and explain the results deduced from the earlier quantitative study.
https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJTC-03-2020-0055/full/html
2021
Achara Khamaksorn
This data paper shows the perspectives by developers of housing on factors of the sustainable construction adoption. The Data was collected by using formal Likert scale questionnaire as main instrument. Simple random sampling was used to assign questionnaires to respondents. Data samples were evaluated using index and rating. The data will provide information on the most variables that considered as main factors for sustainable construction adoption. The importance between variables can provide information that will contribute to the expedition of sustainable practise in housing projects in Malaysia.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352340921008325

Assistant Professor
Jirapat Wanitwattanakosol

Assistant Professor
Napaporn Reeveerakul

Assistant Professor
Pradorn Sureephong

Associate Professor
Ratapol Wudhikarn

Assistant Professor
Pattaraporn Khuwuthyakorn

Assistant Professor
Noppon Choosri

Assistant Professor
Pathathai Na Lumpoon

Assistant Professor
Passakorn Phannachitta

Lecturer
Kittitouch Suteeca

Assistant Professor
Prompong Sugunnasil

Assistant Professor
Pattama Longani

Assistant Professor
Chartchai Doung sa-ard

Lecturer
Phudinun Singkhamfu

Lecturer
Parinya Suwansrikham

Lecturer
Pree Thiengburanathum

Lecturer
Jayakrit Hirisajja

Lecturer
Siraprapa Wattanakul

Lecturer
Jenjira Jaimunk

Lecturer
Apichaka Singjai

Lecturer
Tisinee Surapunt

Lecturer
Porntida Kaewkamol

Lecturer
Pachara Tinamas

Assistant Professor
Krittiya Saksrisathaporn

Lecturer
Thepparit Sinthamrongruk

Lecturer
Waranya Mahanan

Lecturer
Sumalee Sangamuang

Lecturer
Suttinee Sawadsitng

Assistant Professor
Pradorn Sureephong
2022
Danaitun Pongpatcharatrontep
This study develops a new integrated approach for improving deficiencies relating to executives’ intuitive or illogical decisions, mainly found in past intellectual capital management (ICM) methods. 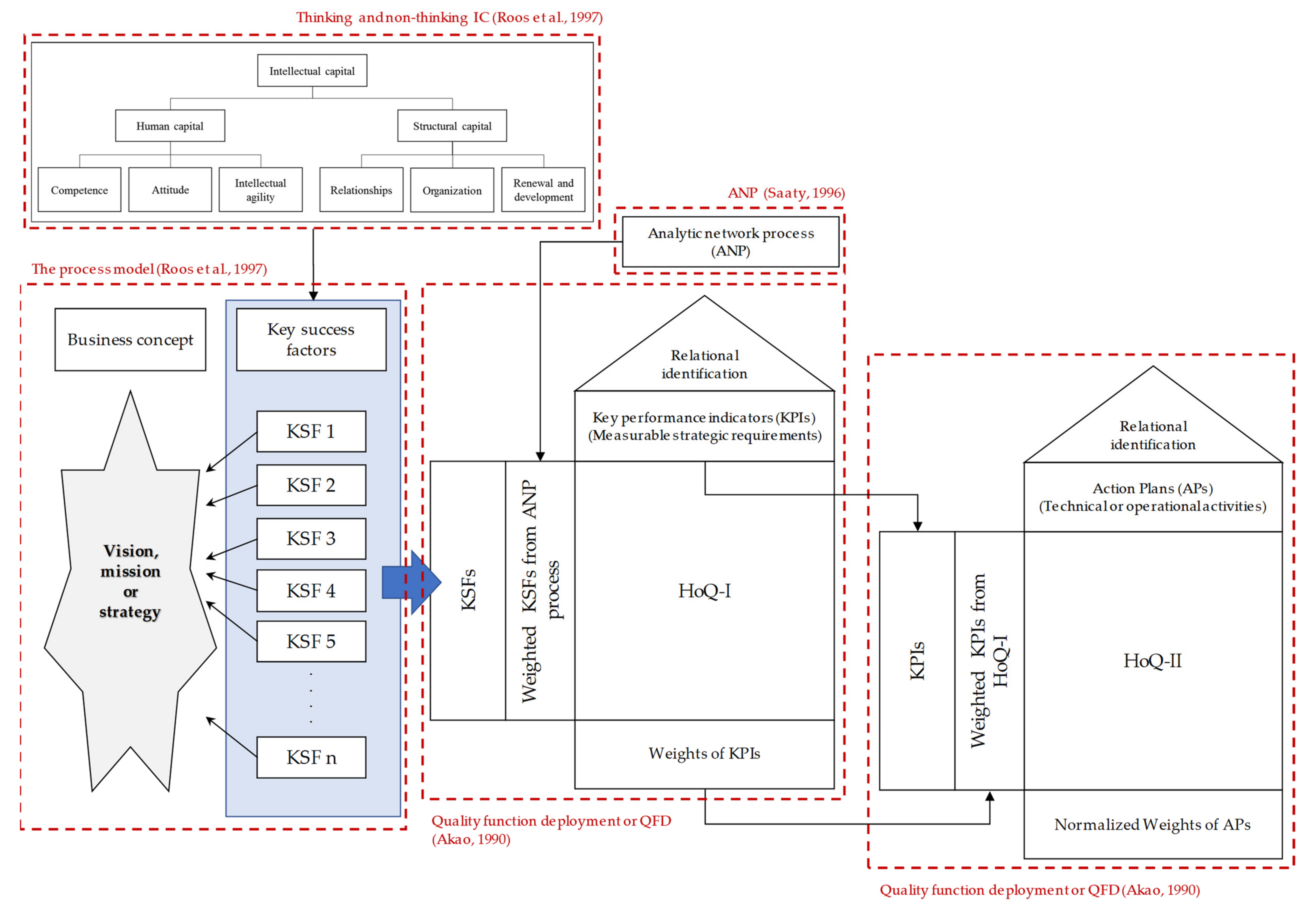
To simultaneously rectify several flaws, the process model of intellectual capital (IC), a traditional ICM method, is integrated using decision science methods—the analytic network process (ANP) and quality function deployment (QFD). The process model of IC is adopted as a core procedure of the proposed ICM approach. ANP is integrated to improve the ability to consider relationships among the IC critical factors and their impacts, while QFD is included to facilitate the systematic consideration and identification of correlations, linkages, and impacts between all IC-related elements from the business concept to strategic plans. The proposed method was applied to two case studies in one real enterprise in Thailand. The results of the implementation reveal the priorities of all IC-related aspects, and the first priority of key success factors (KSFs), key performance indicators (KPIs), and action plans (APs) are all associated with the organization in the structural capital dimension. The results demonstrate that the method may offer advantages with respect to the conceptual expectations and may prioritize critical IC factors and identify their weights. Furthermore, the improved method could indicate the correlations and impacts between related elements, such as critical factors and associated indicators. This study proposes a new comprehensive and systematic management framework by integrating different concepts-decision science methods and the ICM method. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this improved approach has not been explored or proposed in earlier studies.
https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7390/10/4/626
2022
Somkeit Noamna Noamna
The situation of the covid-19 epidemic is a driving force of the global market's demand increase of electronic devices and parts. Entire electronic component manufacturers, especially the transformer manufacturing industry, which is a device that supplies power to many electronic devices, encounters problems in producing products that are unable to keep up with the quickly increasing demand. This research aims to increase the productivity of small transformers by lean approach. The paper depicts processes relevant to improving production processes, reducing waste, and finding unnecessary processes. The method begins with two actions. First, study the current situation in transformer manufacturing of a case study. Second, study the customer order to delivery process using the Value Stream Mapping (VSM) and analyze entire processes of transformer manufacturing to identify standard time by unit work. The main technique is for measuring working time by timing the forward motion with the time measurement method version 2 (MTM-2). The Cause and Effect diagram was displayed with improving guidelines on two operations. First the concept of lean manufacturing was used in principal role, second the ECRS technique (Eliminate, Combine, Rearrange and Simplify) was applied to reduce "waste"as well as to optimize and reduce the manufacturing process of the transformer. The results lead to an increase in the final product per hour from 45 pieces per hour to 75 pieces per hour which increases up to 30% per hour. In addition, the productivity improvements increased the productivity of 3.46 workers per hour to 6.82 per hour (increase of 97.11%) and production time was reduced from 1,109 seconds to 229 seconds (73.04% of productivity).
https://journals.utm.my/aej/article/view/16712/7897
2020
Passakorn Phannachitta
Context: An analogy-based software effort estimation technique estimates the required effort for a new software project based on the total effort used in completing past similar projects. In practice, offering high accuracy can be difficult for the technique when the new software project is not similar to any completed projects. In this case, the accuracy will rely heavily on a process called effort adaptation, where the level of difference between the new project and its most similar past projects is quantified and transformed to the difference in the effort. In the past, attempts to adapt to the effort used machine learning algorithms; however, no algorithm was able to offer a significantly higher performance. On the contrary, only a simple heuristic such as scaling the effort by consulting the difference in software size was adopted. Objective:More recently, million-dollar prize data-science competitions have fostered the rapid development of more powerful machine learning algorithms, such as the Gradient boosting machine and Deep learning algorithm. Therefore, this study revisits the comparison of software effort adaptors that are based on heuristics and machine learning algorithms. Method:A systematic comparison of software effort estimators, which they all were fully optimized by Bayesian optimization technique, was carried out on 13 standard benchmark datasets. The comparison was supported by robust performance metrics and robust statistical test methods. Conclusion:The results suggest a novel strategy to construct a more accurate analogy-based estimator by adopting a combined effort adaptor. In particular, the analogy-based model that adapts to the effort by integrating the Gradient boosting machine algorithm and a traditional adaptation technique based on productivity adjustment has performed the best in the study. Particularly, this model significantly outperformed various state-of-the-art effort estimation techniques, including a current standard benchmark algorithmic-based technique, analogy-based techniques, and machine learning-based techniques.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950584920300872